Call Eric today to schedule a Radon Test!
815-232-3416
The State of Illinois, Illinois Emergency Management Agency (IEMA) program staff informs Illinois citizens about the risk associated with radon and how to reduce levels in their homes.
Access IEMA direct link here.
When Radon Levels in your home are over 4 piC/L, the State of Illinois recommends the installation of a Radon Mitigation System. IEMA monitors statewide screening for indoor radon and they license and regulate the individuals who provide radon measurement and mitigation to the public.
Considering the potential dangers of radon, Bastian Home Inspection encourages radon measurement test whether you're buying, selling, or simply want to have peace of mind.
State of Illinois IEMA Radon Map
State of Illinois IEMA Radon Measurement by Zipcode
State of Illinois IEMA Radon Measurement Chart by County
Radon Levels in Northwest Illinois
State of Illinois IEMA Stephenson County Radon Measurement Average
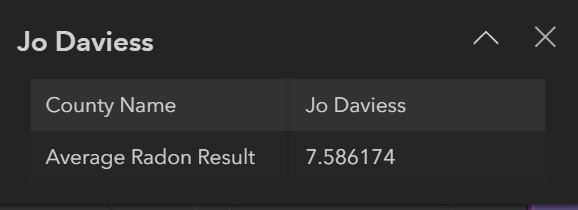
State of Illinois IEMA JoDaviess County Radon Measurement Average
State of Illinois IEMA Carroll County Radon Measurement Average
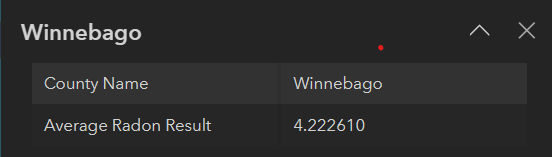
State of Illinois IEMA Winnebago County Radon Measurement Average
Disclosure
Radon measurements above are the average radon testing results as provided by the State of Illinois Licensed Radon Measurement Professionals to IEMA recorded on their interactive map as of January 11, 2023.
What is Radon?
Radon is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas caused by the natural breakdown of uranium in the soil under your home. This hazardous gas seeps into homes from the surrounding soil through porous cement, sump pumps, cracks in the foundation, crawl spaces, etc. Your home acts like a vacuum, drawing radon in.
When inhaled, radon gives off radioactive particles that can damage the cells that line the lung. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer and the number one cause of lung cancer in non-smokers. Radon kills 22,000 people every year in the U.S.
Radon is present in every home. Approximately 30-40% of the homes tested nationwide have elevated levels of radon that need to be corrected, according to the United State Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Any home can have a radon problem: old homes, new homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes without basements. In fact, you and your family are most likely to get your greatest radiation exposure at home. That is where you spend most of your time.
Where does radon come from?
The soil. Radon is produced from the natural decay of uranium that is found in nearly all soils. Uranium breaks down to radium. As radium disintegrates it turns into a radioactive gas…radon. As a gas, radon moves up through the soil and into the air you breathe.
Where is your greatest exposure to radon?
While radon is present everywhere, and there is no known safe level, your greatest exposure is where it can concentrate – indoors, where you spend most of your time – at home. Your home can have radon whether it be old or new, well-sealed or drafty, and with our without a basement.
How does radon enter a home?
Since radon is produced from soil, it is present nearly everywhere. Because soil is porous, radon gas is able to move up through the dirt and rocks and into the air we breathe. If allowed to accumulate, radon becomes a health concern.
Two components that affect how much radon will accumulate in a home are pathways and air pressure. These components will differ from home to home.
Pathways are routes the gas uses to enter your home and found anywhere there is an opening between the home and the soil.
Air Pressure between your home’s interior and the exterior soil is what helps to draw radon gas into the home via the pathways.